Highlights:
- Student loans are a common solution for individuals and families looking to manage the cost of college; however, they’re also a big financial commitment.
- Your credit scores may be significantly impacted depending on how you pay back what you’ve borrowed in student loans.
- Becoming delinquent or defaulting on your student loans can remain on your credit reports for up to seven years.
It’s no secret that a college education is expensive. Student loans are a common solution for individuals and families looking to manage that cost.
However, like all debt, student loans are a serious financial commitment — one that could have a long-term impact on your credit scores. Here’s what to know about the relationship between student loans and your credit scores.
How do student loans work?
Student loans are a type of installment loan, meaning they are a fixed amount of money you borrow and pay back — with interest — in recurring payments.
When students and their families apply for financial aid through the U.S. government, student loans are often offered as a part of a larger financial aid package that may also include scholarships, grants and other kinds of funding. In this case, families fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) and, if approved, the U.S. government acts as your lender.
Private financial institutions also offer student loans, although these often have less favorable terms than the federal options. It’s generally best to take advantage of federal student loans, which usually offer lower, fixed interest rates, deferred payments during enrollment, subsidized interest and even select forgiveness programs.
Private financial institutions also offer student loans, although these often have less favorable terms than the federal options. It’s generally best to take advantage of federal student loans, which usually offer lower, fixed interest rates, deferred payments during enrollment, subsidized interest and even select forgiveness programs.
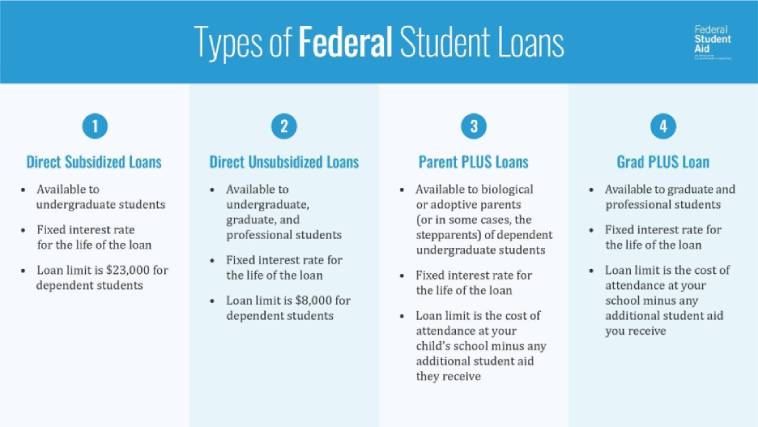
There are several types of student loans:
- Direct Subsidized Loans are available to students who can demonstrate financial need. The government pays for the interest on these loans during a predetermined grace period, usually while the student is still enrolled or recently graduated from college. During this time, borrowers also aren’t required to make payments on the loans.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to all students regardless of need. With these loans, the student is generally responsible for paying interest throughout the life of the loan. As with subsidized loans, borrowers are generally not required to make payments while they are still in school.
Direct PLUS loans are loans made available to the parents of dependent students and to students pursuing graduate or professional degrees. These loans typically have higher interest rates and fees than other types of federal student loans.
How do student loans affect your credit scores?
How do student loans affect credit? Your student loans might affect your credit scores in several different ways.
First, lenders often perform what’s known as a credit check or a hard inquiry to review your credit reports and determine if you’re a suitable candidate for a loan. Hard inquiries help your lenders track how frequently you have applied for credit and can cause your credit scores to temporarily drop each time they appear on your credit report.
Both Direct Subsidized Loans and Direct Unsubsidized Loans are offered to students regardless of their credit history and neither will result in a hard inquiry. A Direct PLUS Loan, however, does require a credit check, so if you’re considering one, your credit scores may take a slight hit.
Second, taking out a student loan can potentially increase your credit scores by diversifying your credit mix, or the different kinds of credit that appear on your credit report. According to lenders, managing several types of debt at once helps show that you’re a responsible borrower.
However, it’s important not to take on too much debt. Your credit utilization ratio, or the amount of revolving credit you’re using divided by the total credit available to you, can have a significant influence on your credit scores as well.
Finally, and most importantly, your credit scores will be significantly impacted depending on how reliably you pay back what you’ve borrowed.
In most scoring formulas, your payment history makes up the largest portion of your credit scores. If you make your required student loan payments on time and avoid going into default, your student loans may help you establish or build your credit history. Lenders want to see that you have experience repaying any funds you borrow, and your student loans can help you show just that.
How do missed payments affect your credit scores?
If you miss a payment, you have 90 days before the loan is considered delinquent. After that time, missed payments appear on your credit reports and your credit scores may drop.
If you continue to miss payments, you run the risk of the loan going into default, which can further decrease your credit scores. You could also lose access to certain debt relief options, and you might be required to pay steep collection fees or have your wages garnished.
How long do student loans stay on your credit reports?
Delinquency or default can remain on your credit reports for up to seven years. During that time, lenders may be reluctant to offer you additional credit.
If you’re struggling to meet your federal loan obligations, research options for repayment aid. For example, you might be eligible for lower monthly payments through an income-driven repayment (IDR) plan. Talk to your loan servicer to find the best solution for you. Private loans are often less lenient regarding delinquency and default, so it’s important to know the terms and conditions of your loan.
Best strategies to pay off your student loans
It’s important to treat student loans as you would any other debt to avoid negatively affecting your credit scores.
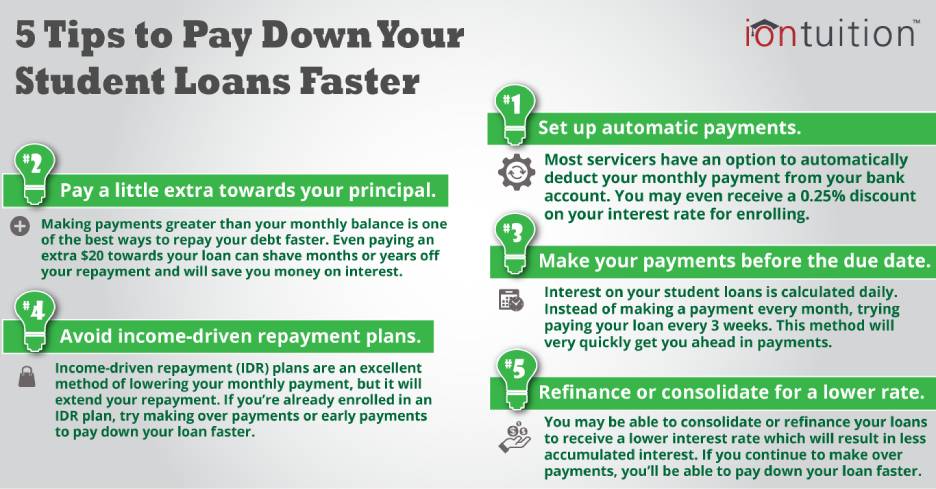
Make payments during your grace period. Making payments on your loan — even during the grace period — will reduce the total amount you’ll have to pay in interest.
Pay more than the minimum. If you can afford it, pay more than the minimum monthly payment to reduce your interest cost over time.
Consider enrolling in autopay. Your loans may offer the option of making monthly payments automatically, which helps ensure you’re paying on time. In some cases, automatic payments can also reduce your interest rate.
Be aware of your repayment options. If you can’t make a payment, contact your lender immediately. Make sure you know the debt relief programs that might be available to you, such as IDR plans or loan forgiveness.
Student loans are an important step toward funding an education for millions of student borrowers. Just be sure that you understand how obtaining a student loan could impact your credit scores. Careful repayment can help keep your credit scores in good shape through graduation and beyond.
For a free monthly VantageScore 3.0 credit score and Equifax credit report, you can create a myEquifax account and click “Get my free credit score” on your myEquifax dashboard to enroll in Equifax Core Credit™. A VantageScore is one of many types of credit scores. You can also get free credit reports annually from the three nationwide consumer reporting agencies (Equifax, TransUnion and Experian) at AnnualCreditReport.com.